System Design
On September 3, 2018 in interviewing • 2 minutes read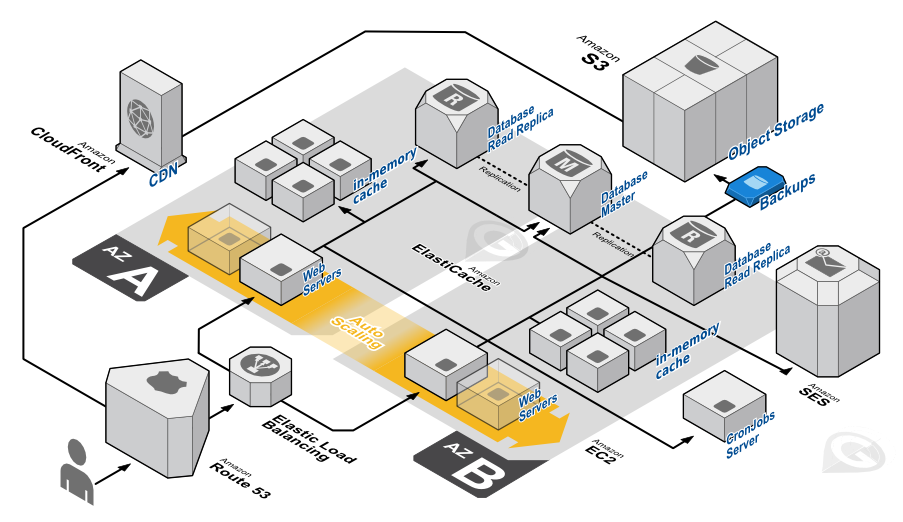
An algorithm for solving system design interviews:
- Requirements
- Math
- Data in (Concurrency) X Data out
- Latency x Throughput
- Main bottlenecks
- Availability
- Performance (Response time, Scalability, CPU / IO / Network bound applications)
- Confidentiality (Encryption)
- High level design
- Evaluate use cases: what is the flow for each of them?
- This usually results in, at a minimum:
- Application layer & responsibilities
- Database layer & responsibilities
- Detailed design
- Start small & grow big
- Profiling: Estimate & test load for every use case and identify bottle necks
- Requests per second resulting in:
- Write per second (Where? What?)
- Read per second (Where? What?)
- Handy reference: 2.5 million seconds per month
- Requests per second resulting in:
- Horizontal X Vertical Scaling - DNS Server: Resource allocation
- Resolves the text URL for a particular web resource to the TCP-IP address of the system or service: Must be quick
- Directs to either:
- Proxies / Firewalls
- CDNs: Geographically distributed for static assets: templates , themes , images, etc.
- Cloud Backend: Web & App functionalities - Load Balancing: Horizontal scaling & Redundancy
- Software X Hardware
- Zero Uptime & Increased Performances:
- Responsibilities:
- Health checks
- Load distribution algorithms
- Challenge: Session Management
- Sticky sessions X External storage - Web application layer: Serves dynamic content & renders HTML
- Multiple instances serve independent requests
- Off-Line Processing: Reduces latency and/or handles batch processing
- Message Queues: Queue work & process in parallel
- Scheduling System Tasks: Perform recurring tasks offline
- Specialized infrastructure: Map-Reduce for big data - Content Performances: Improves use of resources
- Caching
- Where?
- Which layer? Application X Dedicated X Database
- In memory for vertical scaling?
- Writethrough cache: Write to cache and then continously push to DB
- Challenge: Concurrency & Cache Invalidation at App Layer - Manageability: Platform & Management Layer
- Where?
- Separates the DB and Web application: Scale the pieces independently.
- Independent API: Re-use layers for different purposes
- Includes:
- Automation & Cost Improvement:
- Just-in-time Infrastructure
- Reduces human interaction & errors
- Monitoring and Alerts
- Log files
- Automation & Cost Improvement:
- Development practices:
- Source control
- Multi-step deployment - Database Layer
- Type: Relational X Graph X Key-Value stores
- Availability: Master and Standby
- Performances:
- Master and Read Replicas
- Horizontal Scaling of Data Storage: Sharding for storing data on separate databases
- Per Table Indexes: Avoid searches in your data
- Data Loss: Backups
- Security
- Think of Confidentiality / Integrity / Availability
- Prevention: Lock out attackers
- Shared vs Dedicated Instances
- Access Control & Authentication:
- Active Directory
- Two factor authentication
- Firewalls (Security Groups) between layers of architecture
- Data & Traffic Encryption - Detection: Find anomalous behaviour
- Baselining
- DDoS mitigation - Reaction: Admins & System take appropriate measure to stop attack
- Alarms
- Honeypots
- Low Level
- Database Schema
- RESTful API
Related
Other Interviewing Pages
- September 11, 2018: Mindmapping STAR